Learn to Use Multiplier and ModelSim to Output- FPGA Board for Beginner – FPGA Tutorial – Experiment 6
Experiment 6 Use of Multipliers and ModelSim Simulation
6.1 Experiment Objective
- Learn to use multiplier
- Use ModelSim simulation to design output
6.2 Experiment Implement
- 8×8 multiplier, the first input value is an 8-bit switch, and the second input value is the output of an 8-bit counter.
- Observe the output in ModelSim
- Oberseve the calculation results with a four-digit segment display
6.3 Experiment
Since the simulation tools and the new IP core are used here, there is no introduction or design part of hardware.
6.3.1 Introduction of Program
ModelSim is an HDL language simulation software. Programs can be simulated to achieve inspection and error correction. ModelSim experiment, different from the previous experiment, when building the project, the simulation tool to be used needs to be added in the EDA tool selection window. See Figure 6.1.
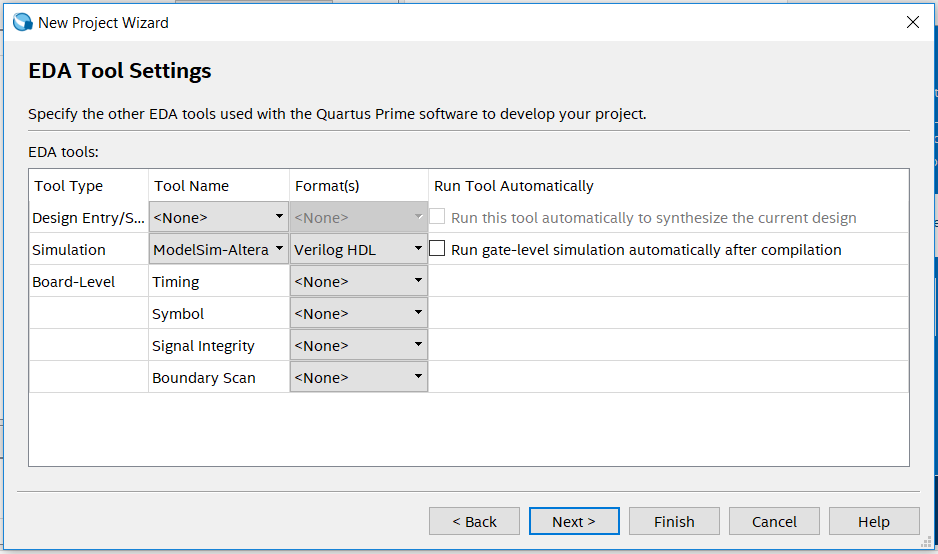
Figure 6.1 EDA tool setting
Only one counter, one PLL and one multiplier are used in the program. Only the multiplier is introduced here.
The first step: the establishment of the main program framework
module mult_sim ( input inclk, input rst, input [7:0] sw, output [15:0] mult_res, output reg [7:0] count );
The value of the switch is used as the first input of the multiplier, the value of the counter is the second input, and the result of the calculation is output.
The second step: the multiplier IP core setting steps are as follows:
- After adding the LPM_MULT IP (IP Catalog > Library > Basic Functions > Arithmatic > LPM_MULT) and saving the path, the setting window of the multiplier is popped up, as shown in Figure 6.2, and the two input data is set to eight bits as required.
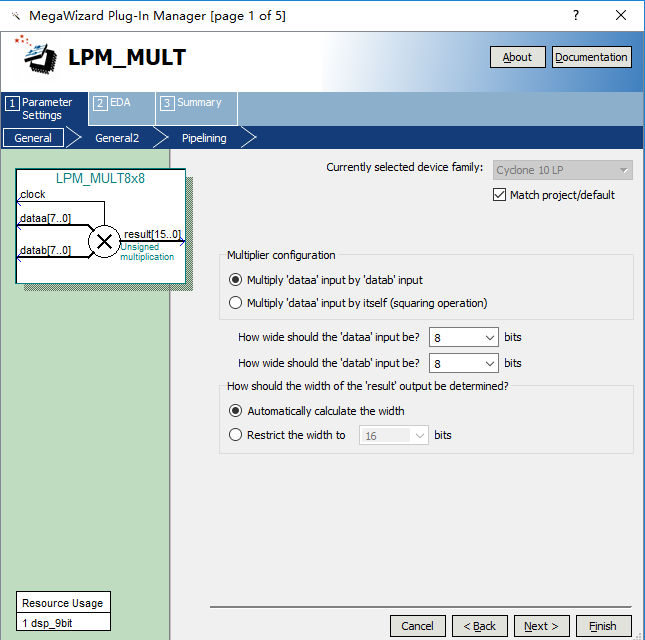
Figure 6.2 mult setting 1
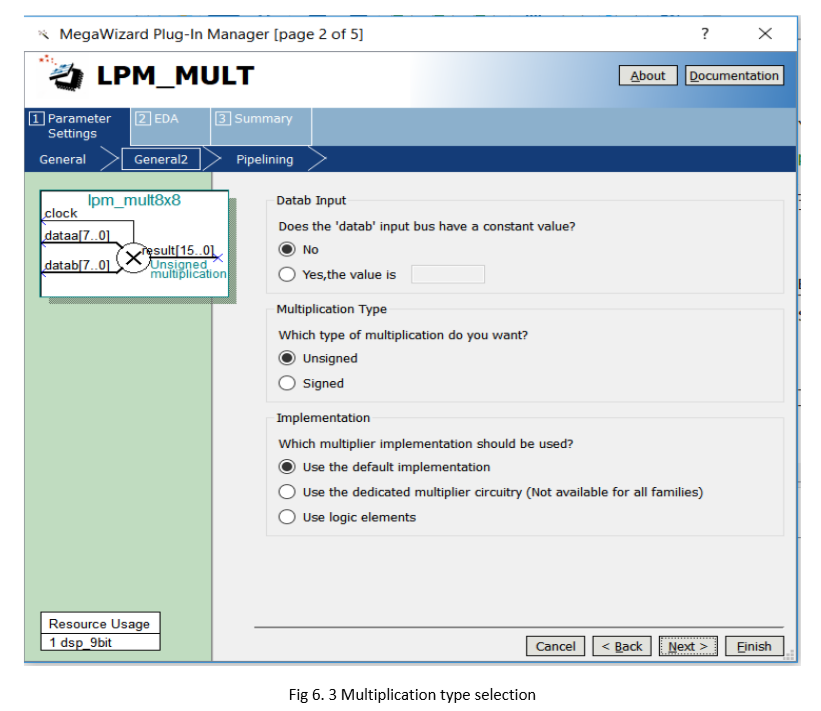
- Select the multiplication type to be Unsigned. See Figure 6.3.
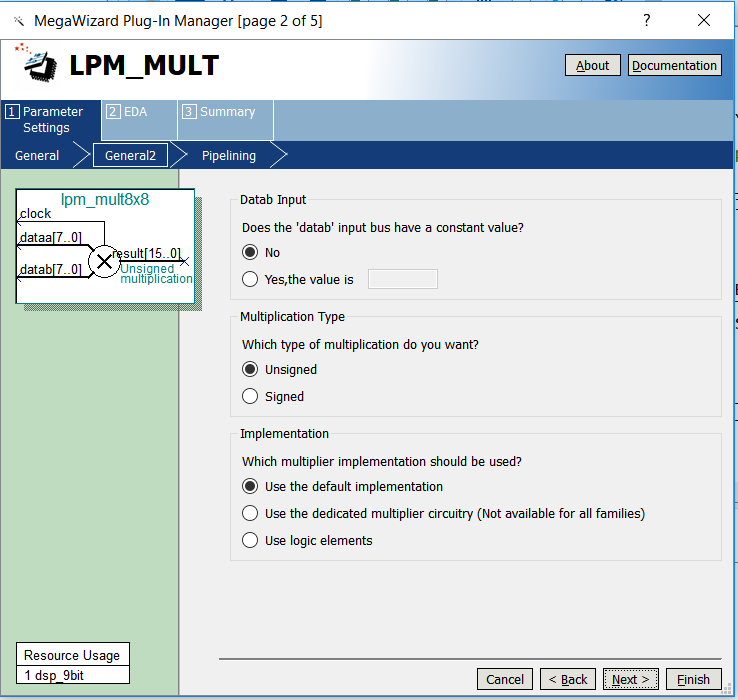
Figure 6.3 mult setting 2
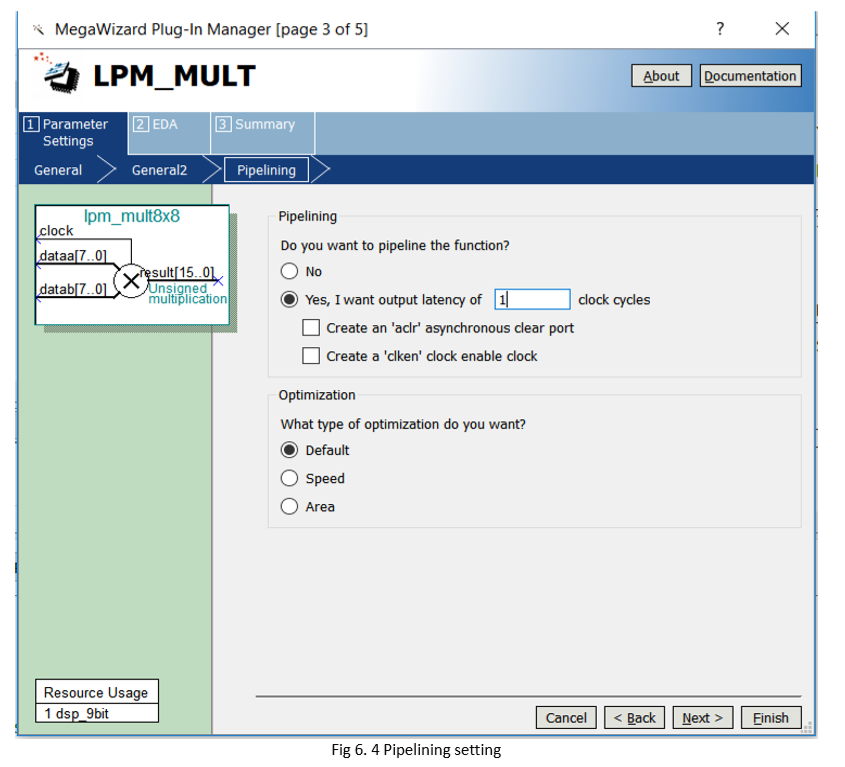
- Select the pipeline to speed up the operation, as shown in Figure 6.4.
- Select others to be default.
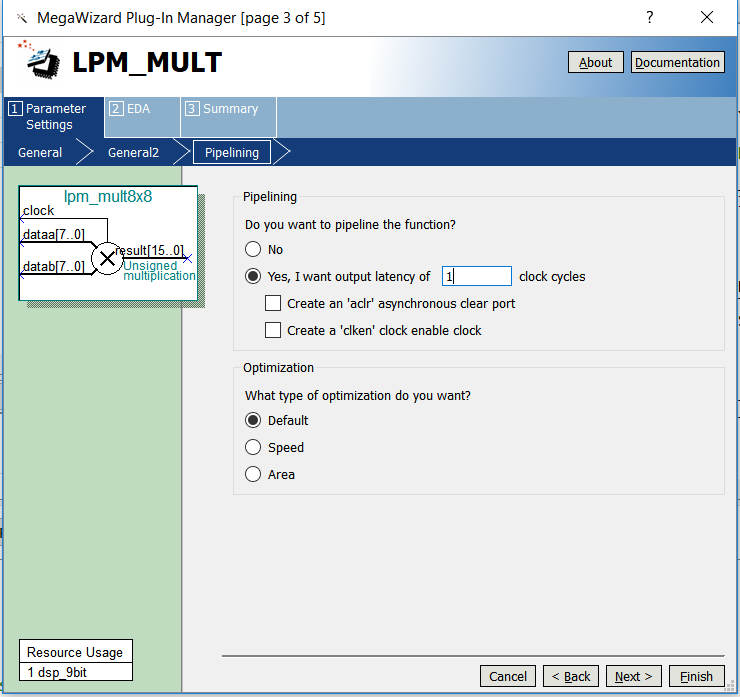
Figure 6.4 mult setting 3
8×8 multiplier instantiation:
reg sys_clk; mult_8x8 mult_8x8_inst ( .clock (sys_clk), .dataa (sw), .datab (count), .result (mult_res) );
6.4 Use of ModelSim and the Experiment Verification
Here, ModelSim simulation is used to verify the experiment.
Method 1: Simulation based on waveform input
- Click the menu bar Tools > Options, as shown in Figure 6.5, click OK.
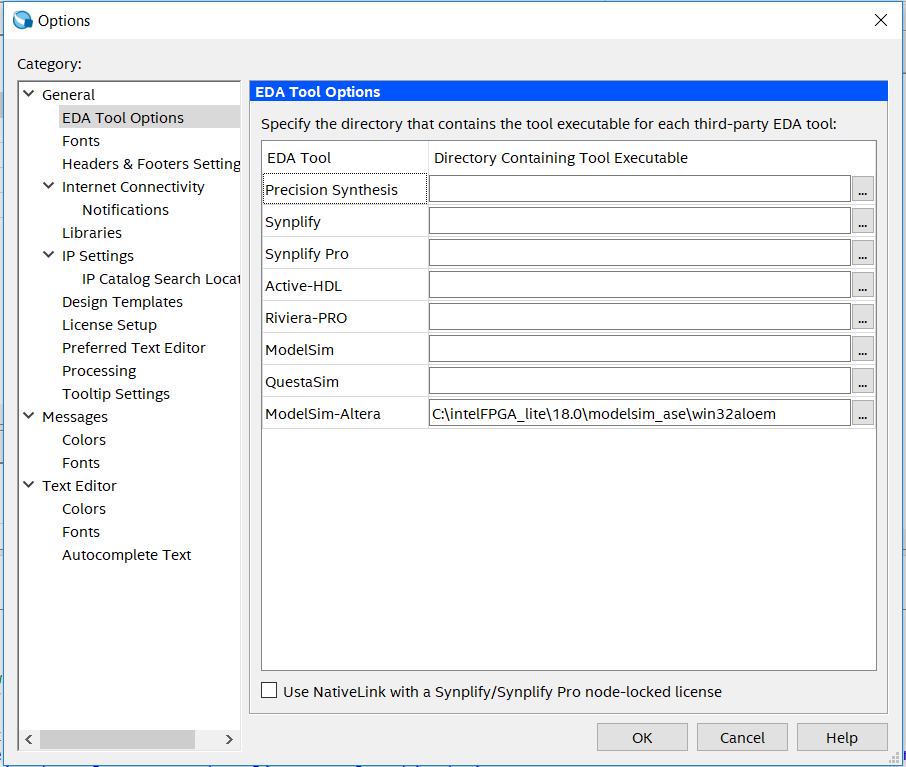
Figure 6.5 Select ModelSim-Altera path
- Tools > Run Simulation Tool > RTL Simulation to start simulation. See Figure 6.6.
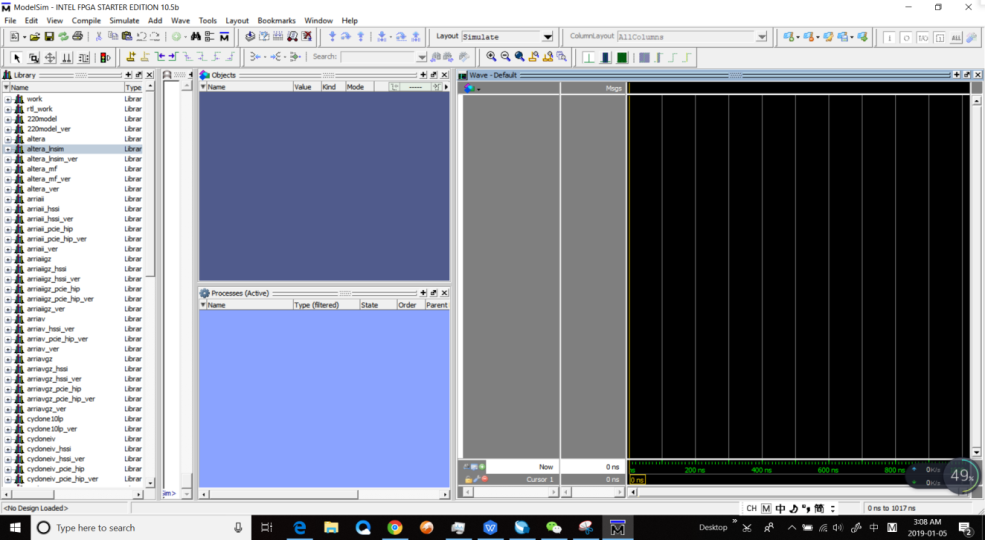
Figure 6.6 ModelSim window
- Set ModelSim
- Simulate > Start Simulation
- In the popup window, add libraries under Libraries tag. See Figure 6.7.
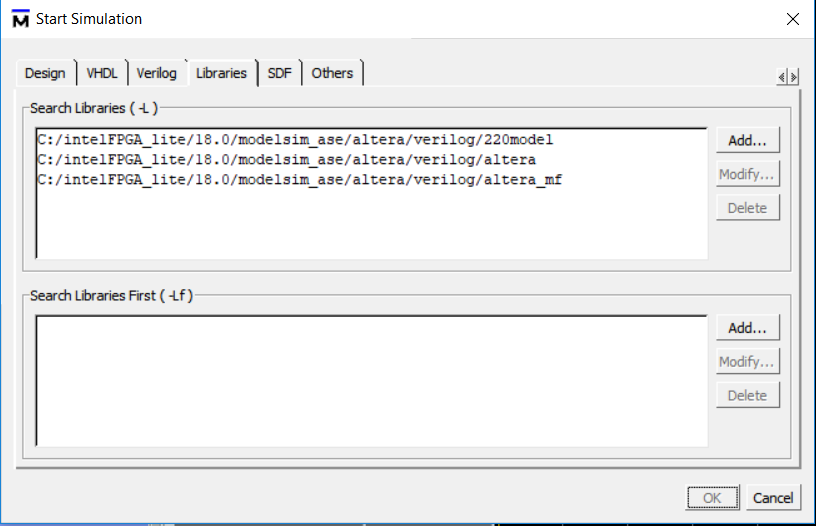
Figure 6.7 Add simulation libraries
- Under Design tag, choose simulation project mult_sim and click OK. See Figure 6.8.
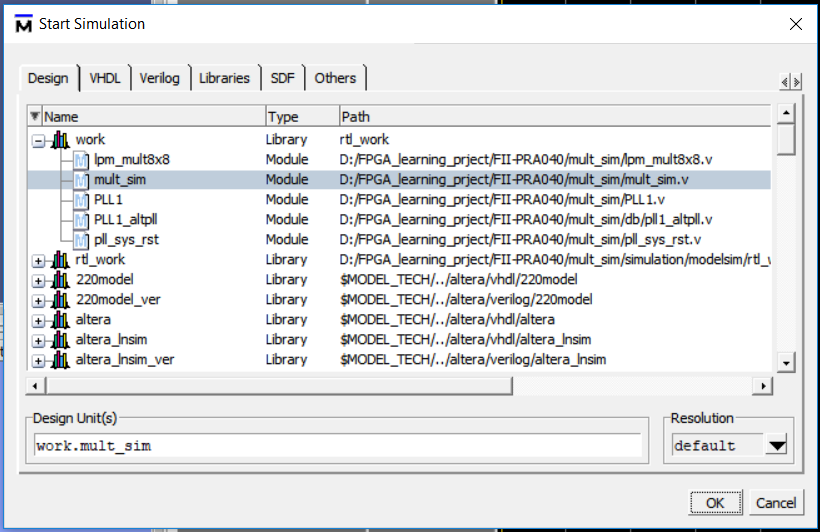
Figure 6.8 Choose the project to simulate
- In the Objects window, choose all the signals and drag them to Wave window. See Figure 6.9.
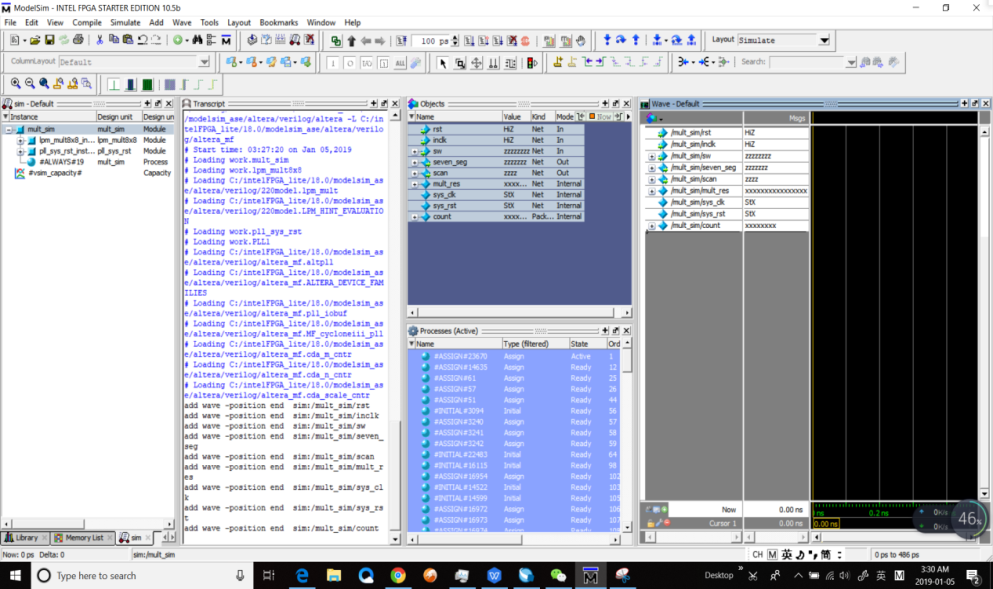
Figure 6.9 Add observation signals
- Set the signals in Wave, right click any signal and a selection window will occur. See Figure 6.10.
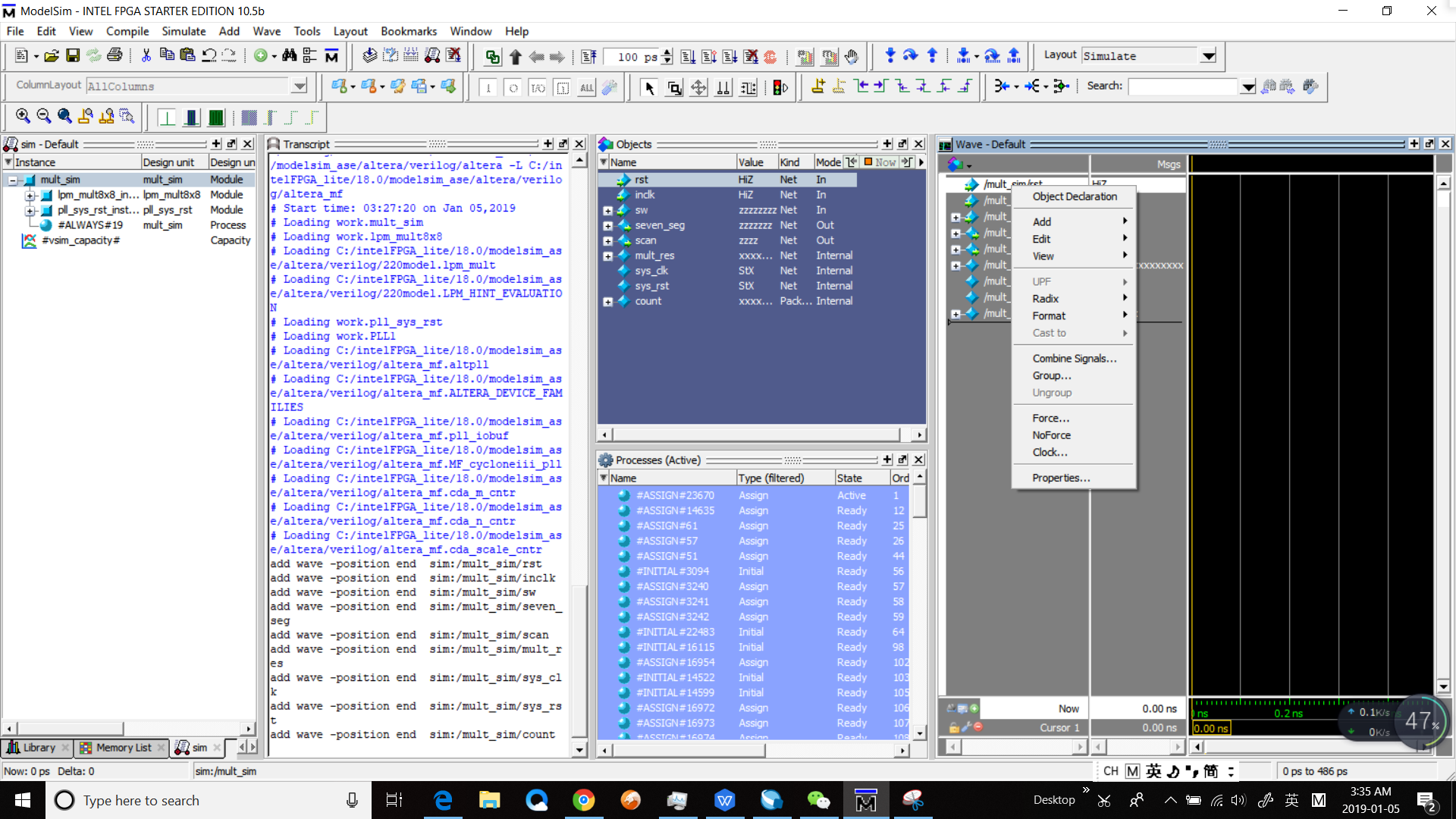
Figure 6.10 Set the signals
- Logical signals select Force and select Clock for clock signals
- Set rst siganl. See Figure 6.11.
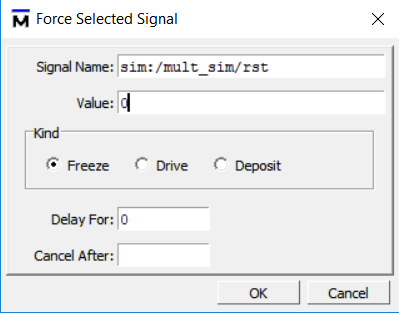
Figure 6.11 Set rst signal
- Set Inclk signal. See Figure 6.12.
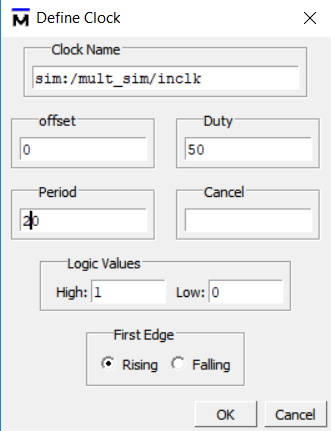
Figure 6.12 Set inclk signal
- Set sw signal. See Figure 6.13.
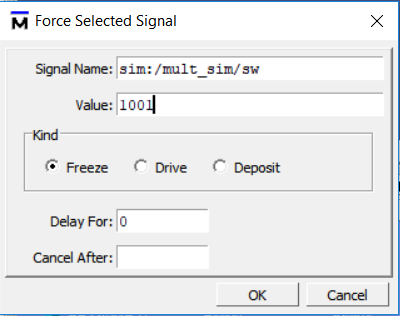
Figure 6.13 Set sw signal
- Run simulation. In the tool bar, set the simulation time to be 100 ns. Click the Run icon to run the simulation. See Figure 6.14.
Figure 6.14 Set the simulation time
- Observe the simulation result. See Figure 6. 15.
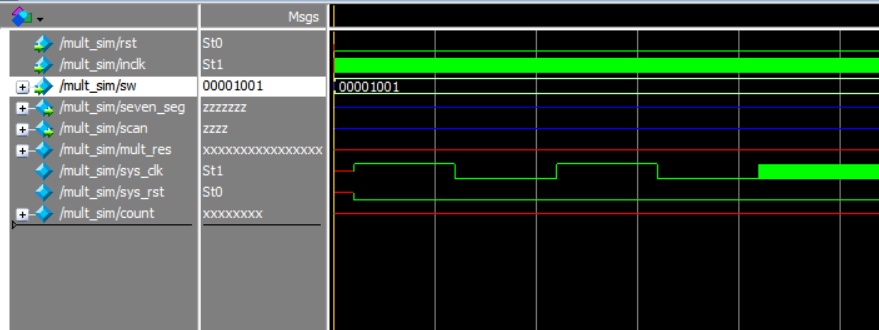
Figure 6.15 Simulation result
- Result analysis
- Counter count does not have a valid result, instead, unknow result XXXXXX is gotten.
- sys_rst does not reset signals. It changes from X to 0
- Add pll_locked signal to the wave, and re-simulate
- In Figure 6.16, before PLL starts to lock, the sys_clk already has a rising edge, so PLL_locked signal is just converted from low to high. There is no reliable reset is formed.
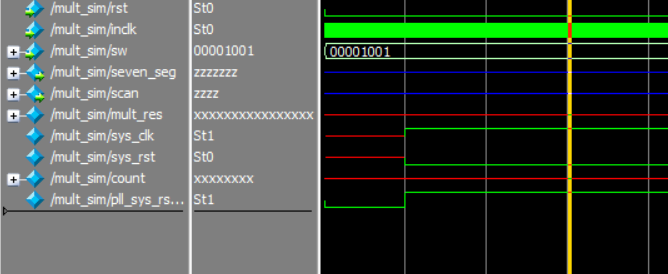
Figure 6.16 Re-simulation result
- Solution
- Define sys_rst to be 1’b1
- Use external rst signal to provide reset
Here method a is adopted. The revised code is as follows:
module pll_sys_rst( input inclk, output sys_clk, output reg sys_rst = 1'b1 );
- Recompile the simulation
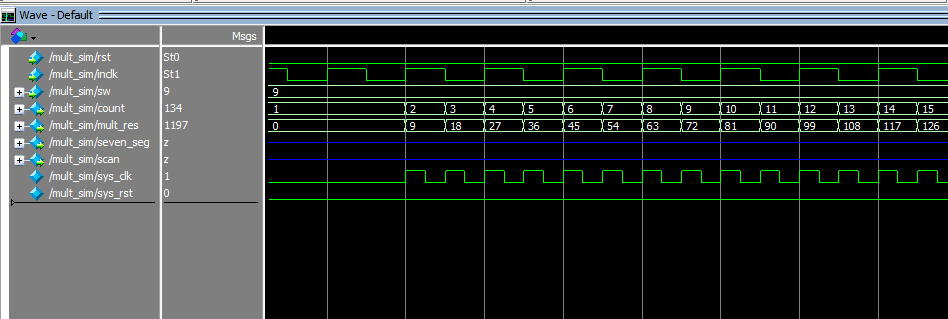
Figure 6.17 Recompile the simulation
Since waveform editing efficiency is relatively low, the use of simulation testbench file is encouraged.
Method 2: Write a testbench file for simulation
- Name a new Verilog HDL file tb_mult.v.
- The code is as follows:
`timescale 1ns/1ps
module tb_mult;
reg rst;
reg clk;
reg [7:0] sw;
wire [7:0] count;
wire [15:0] mult_res;
// S1 is the instance of simulation module
mult_sim S1(
.rst (rst),
.inclk (clk),
.sw (sw),
.count (count),
.mult_res (mult_res)
);
// Define the clock required for the simulation and display the results in text form
always begin
#10 clk = ~clk;
$monitor ("%d * %d = %d", count, sw, mult_res);
end
//Set the simulation condition
initial begin
rst = 0;
clk = 1;
#10 sw = 20;
#10 sw = 50;
#10 sw = 100;
#10 sw = 101;
#10 sw = 102;
#10 sw = 103;
#10 sw = 104;
#50 sw = 105;
//Stop the signal
#1000 $stop;
end
endmodule
When writing the testbench file, first mark the time unit of the simulation at the beginning, this experiment is 1 ns, then instantiate the project that needs to be simulated into the testbench file, define the clock cycle and the simulation conditions, and stop the simulation after a certain time. This simulation stops after 1000 clock cycles.
After the compilation, the testbench file is added to the ModelSim for simulation, the specific steps are as follows:
- Set the testbench file: Assignments > Settings. See Figure 6.18.
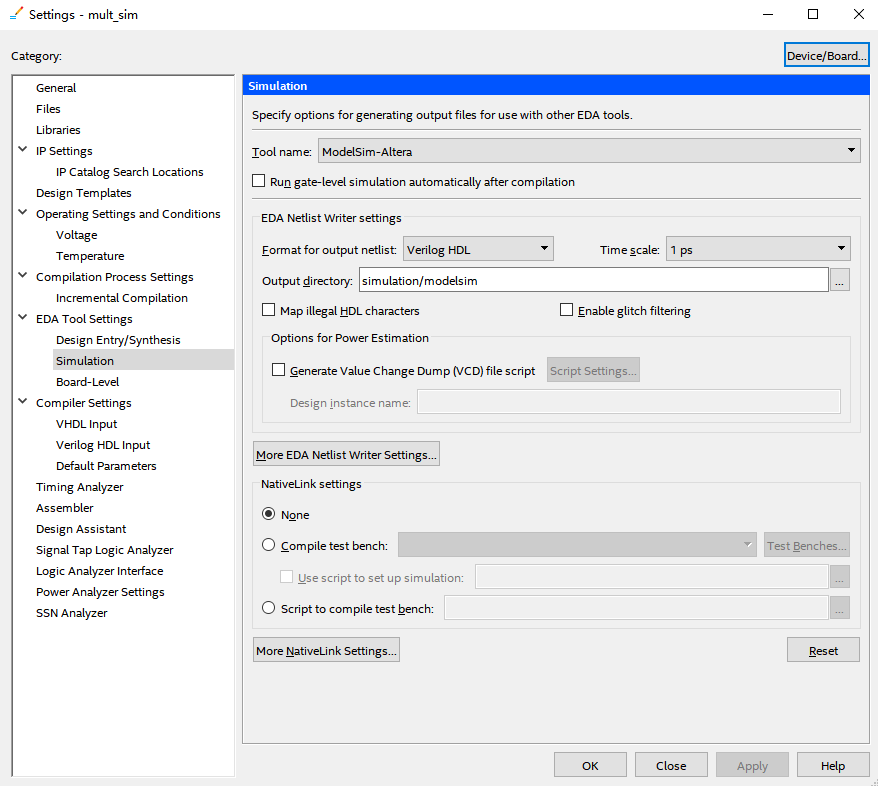
Figure 6.18 Simulation setting 1
- In Compile test bench, click Test Benches to add tb simulation file. See Figure 6.19.

Figure 6.19 Simulation setting 2
- Click New, input the Test bench name. Make the name be consistent with tb file. See Figure 6. 20.
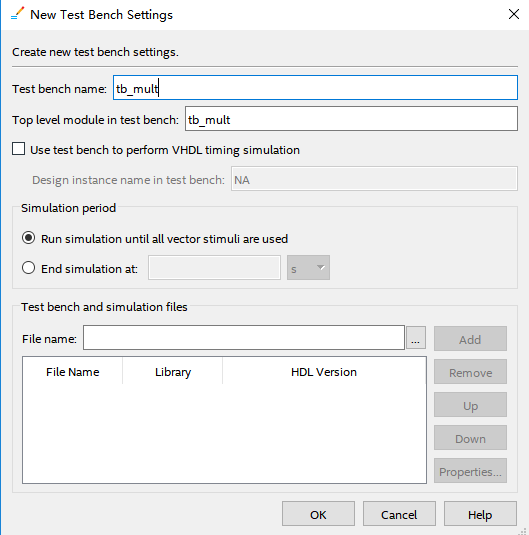
Figure 6.20 Simulation setting 3
- Click the red ellipse to add the test bench file. Find tb_mult.v file written before.
- Click Add to add the file. Click OK (three times) to finish the setting. See Figure 6.21.
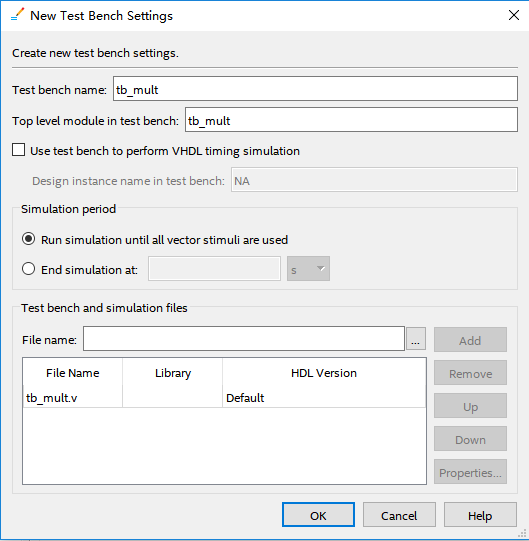
Figure 6.21 Simulation setting 4
Repeat previous step, to start ModelSim to simulate. See Figure 6.22.
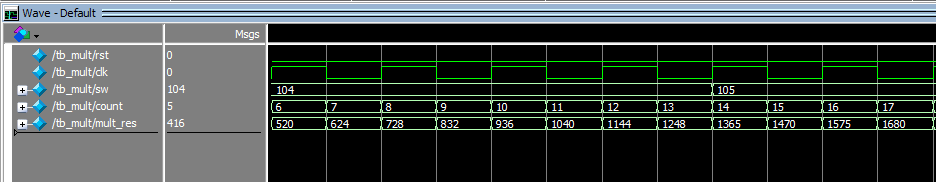
Figure 6.22 Waveform output
After a certain delay, outputs will display in Transcript. See Figure 6.23
Because the result of the operation will be one clock cycle later than the input, the multiplier and the result will differ by one line, which does not seem to match, but does not affect the analysis of the experimental results.

Figure 6.23 Text displays operation result
Summary and Reflection
Try to use the switch as the input to the multiplier. The upper four digits are one number, the lower fourth digits are a number, and the two numbers are multiplied to output the result.
Old Version (2019)
6.1 Experiment Objective
- Learn to use multiplier
- Use ModelSim to output
6.2 Experiment Requirement
-
8×8 multiplier. The first input is 8-bit switch, and the second input is the output of an 8-bit counter.
-
Observe the output in ModelSim.
-
Observe the calculation result on 4 segment decoders.
6.3 Experiment
-
Build a new project mult_sim
Different from what we did before, we use EDA simulation. The actual setting is shown in Fig 6. 1
- Design procedure
-
-
Create a new file named mult_sim.v
-
Add PLL, set the clock input frequency is 50 MHz, and the output is 100 MHz
-
In the right of the main interface, find Installed IP > Library > Basic Functions > Arithmetic > LPM_MULT IP. An interface will pop up. See Fig 6. 2
-
-
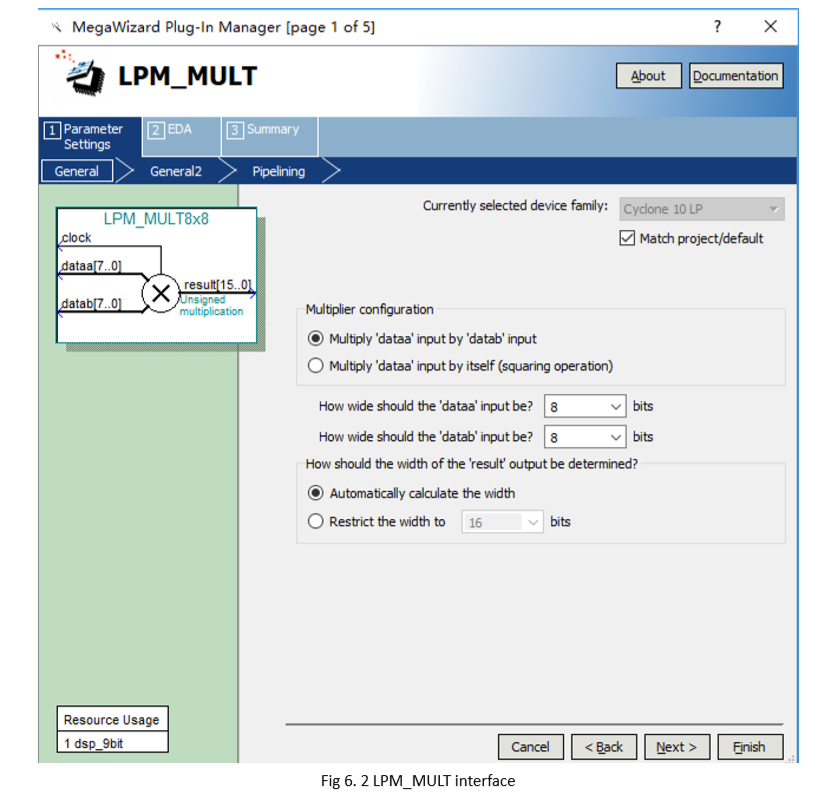
LPM_MULT_interface
- The top level file is as follows
module mult_sim ( input inclk, input rst, input [7:0] sw, output [6:0] seven_seg, output [3:0] scan, output [15:0] mult_res, output reg [7:0] count ); wire sys_clk; wire sys_rst; always @ (posedge sys_clk) if(sys_rst) count <= 0; else count <= count + 1; pll_sys_rst pll_sys_rst_inst( .inclk (inclk), .sys_clk (sys_clk), .sys_rst (sys_rst) ); mult_8x8 mult_8x8_inst ( .clock (sys_clk), .dataa (sw), .datab (count), .result (mult_res) ); endmodule
-
ModelSim simulation
-
Simulation based on waveform inputs
-
Tool > Option. In the popup window, under General, find EDA Tool Options. In ModelSim-Altera, find the correct path. See Fig 6. 5
Fig 6. 5 Set the correct path for ModelSim-Altera
- Tool > Run Simulation Tool > RTL Simulation. See Fig 6. 6
Fig 6. 6 Simulation interface
- Set ModelSim
- Simulate > Start Simulation
- In the popup window, add libraries under Libraries tag. See Fig 6. 7
- Under Design tag, choose simulation project mult_sim and click OK. See Fig 6. 8
Fig 6. 7 Add simulation libraries
Fig 6. 8 Choose the project in simulation
- In the Objects window, choose all the signals and drag them to Wave window. See Fig 6. 9
Fig 6. 9 Add observation signals
- Set the signals in Wave, right click any signal and a selection window will occur. See Fig 6. 10
Fig 6. 10 Set the signals
- For logical signals select Force and select Clock for clock signals
- Set rst signal. See Fig 6. 11
Fig 6. 11 Set rst signal
- Set Inclk signal. See Fig 6. 12
Fig 6. 12 Set inclk signal
- Set sw signal. See Fig 6. 13
Fig 6. 13 Set sw signal
-
Run simulation. In the tool bar, set the simulation time to be 100 ns. Click the Run icon to run. See Fig 6. 14
Fig 6. 14 Set the simulation time
- Observe the simulation result. See Fig 6. 15
Fig 6. 15 Simulation result
-
Result analysis
-
Counter count does not have a valid result, instead, unknow result XXXXXX is gotten.
-
sys_rst does not reset signals. It changes from X to 0
-
Add pll_locked signal to the wave, and re-simulate
Fig 6. 16 Re-simulation result
-
In Fig 6. 16, before PLL starts to lock, the sys_clk already has a rising edge, so PLL_locked signal is just converted from low to high. There is no reliable reset is formed.
- Solution
Method 1: Define sys_rst to be 1’b0;
module pll_sys_rst(
input inclk,
output sys_clk,
output reg sys_rst =1’b1
);
Method 2: Use external rst signal to procide reset
Here, method 1 is adopted
Fig 6. 17 Recompile the simulation
- Recompile the simulation. See Fig 6. 17
-
Since waveform editing efficiency is relatively low, the use of simulation testbench file is encouraged. Name a new Verilog HDL file tb_mult.v.
`timescale 10ns/1ns
module tb_mult; //Define the simulation signal
reg rst;
reg clk;
reg [7:0] sw;
wire [7:0] count;
wire [7:0] seven_seg;
wire [3:0] scan;
wire [15:0] mult_res;
mult_sim S1( // S1 is the instance of simulation module
.rst (rst),
.inclk (clk),
.sw (sw),
.seven_seg (seven_seg),
.scan (scan),
.count (count),
.mult_res (mult_res)
);
always #5 clk = ~clk;
initial //Initialize the simulation signals
begin
rst = 0;
clk = 1;
#5 sw = 20;
#10 sw = 50;
#10 sw = 100;
#10 sw = 101;
#10 sw = 102;
#10 sw = 103;
#10 sw = 104;
#50 sw = 105;
$monitor(“%d * %d=%d”, count, sw, mult_res);
#1000 $stop;
end
endmodule
- Compile and simulate
- Only choose Start Analysis & Elaboration, do not choose either compilation or synthesis one. See Fig 6. 18
Fig 6. 18 TB file analyzing
- Set the testbench file: Assignments > Settings. See Fig 6. 19
Fig 6. 19 Simulation setting 1
Go to Simulation, For Tool name, select ModelSim-Altera. In Compile test bench, click Test Benches to add tb simulation file. See Fig 6. 20
Fig 6. 20 Simulation setting 2
Click New, input the Test bench name. Make the name be consistent with tb file. See Fig 6. 21.
Fig 6. 21 Simulation setting 3
Click the red ellipse to add the test bench file. Find tb_mult.v file written before. Click Add to add. Click OK (three times) to finish the setting. See Fig 6. 22
Fig 6. 22 Simulation setting 4
- Repeat previous step, to start ModelSim to simulate. See Fig 6. 23
Fig 6. 23 Waveform output
- After a certain delay, outputs will display in Transcript. See Fig 6. 24
Fig 6. 24 Text displays operation result